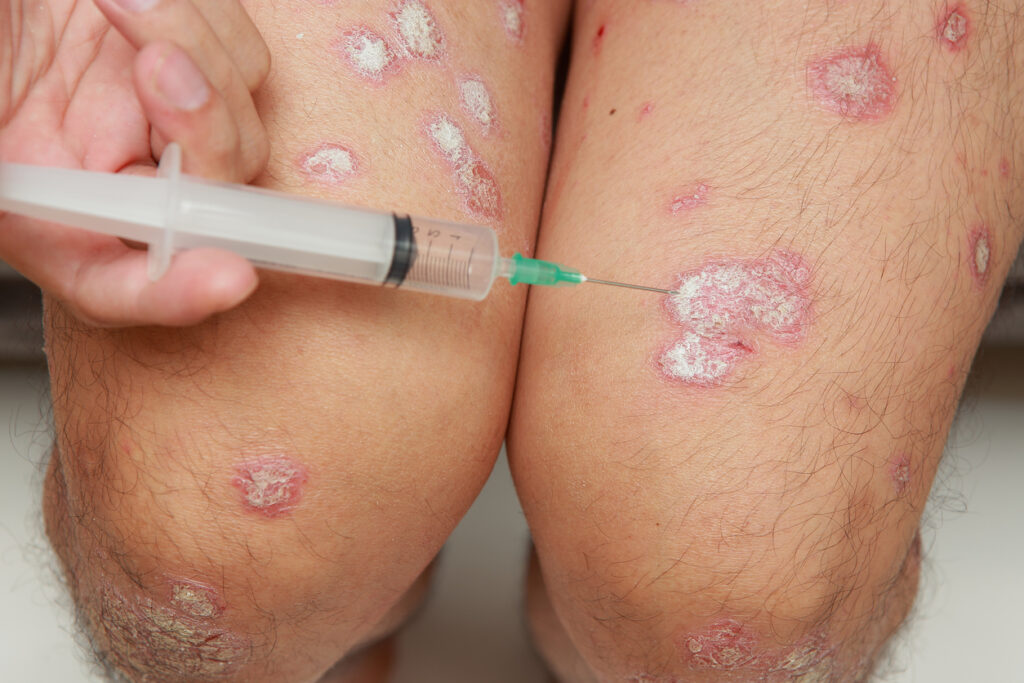
Biologics have revolutionized the treatment of inflammatory skin diseases but can trigger immune drift, shifting CD4+ T-cell polarization and causing adverse skin reactions.
Researchers reviewed CD4+ T Cell-mediated immune drift and mechanisms in the treatment of immune inflammatory skin diseases with biological agents in Future Integrative Medicine.
Here’s what they found:
Mechanisms of Immune Drift by Biologic Class
- TNF-α Inhibitors: Etanercept, Infliximab, Adalimumab
- Mechanism: Blocking Th1 pathway → Loss of Th1-mediated suppression of Th2 → Th2 dominance
- Clinical Manifestations: Eczema-like lesions (2%–20% incidence in non-dermatologic diseases; 1%–6% in psoriasis)
- Evidence: Elevated interleukin (IL)-5/IL-13 in lesions; exacerbated atopic dermatitis in Crohn’s disease patients
- IL-17 Inhibitors: Secukinumab (Cosentyx, Novartis), Ixekizumab (Taltz, Lilly)
- Mechanism:
- Suppression of Th17 → Th2/Th22 imbalance (elevated IL-22)
- Reduced antimicrobial peptides → Staphylococcus aureus colonization → Barrier disruption
- Overexpression of IL-17C (linked to Th2 inflammation)
- Clinical Manifestations: Eczema (2.2%–12.1%), bullous pemphigoid (Th2-driven)
- IL-12/23 Inhibitors: Ustekinumab, Guselkumab (Tremfya, Janssen Biotech, Inc)
Mechanism: Blocking p40 subunit → Impaired Th1/Th17 differentiation → Compensatory Th2 activation
- Clinical Manifestations: Atopic dermatitis flare (especially in patients with a history of atopy/elevated IgE)
- IL-4/13 Inhibitors: Dupilumab (Dupixent, Sanofi & Regeneron)
- Mechanism: Blocking IL-4Rα → Suppressed Th2 → Unchecked Th1/Th17 expansion
- Clinical Manifestations: Psoriasiform lesions (3%–5%), polymyalgia rheumatica (Th17-mediated), ulcerative colitis (Th1-driven)
- PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors
- Mechanism:
- T-cell activation → IFN-γ release → Epidermal dyshomeostasis
- Shift from M2 to M1 macrophages → TNF-α/IL-12 release → Th17 expansion
- Clinical Manifestations: Psoriasiform eruptions (high prevalence in cancer patients)
Clinical Management of Immune Drift
Risk Identification
- High-risk patients: History of atopy, asthma, psoriasis, or elevated serum IgE
- Monitoring: Regular assessment of cytokine profiles (e.g., Th2 cytokines for TNF-α inhibitor users)
Therapeutic Strategies
- Mild Reactions: Topical glucocorticoids or antimicrobial ointments
- Persistent Reactions:
- Biologic suspension/switching (e.g., dupilumab for IL-17-induced eczema)
- Immunomodulators: Methotrexate, cyclosporine
- Phototherapy for psoriasiform lesions
- Emerging Approaches:
- Natural Compounds: Curcumin/resveratrol activate aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR), restoring barrier function and suppressing Th2 cytokines
- Nanotechnology: Epidermal-targeted carriers enhance drug delivery, minimizing systemic immune drift
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRGF): Anti-inflammatory modulation in atopic dermatitis/psoriasis
Limitations and Future Directions
- Knowledge Gaps: Non-classical pathways (e.g., Th9, Th22) underexplored
- Precision Medicine Goals:
- Biomarker development (e.g., IgE, cytokine panels) for risk stratification
- Dual-target biologics to prevent compensatory pathway activation
- Dynamic immune monitoring via liquid biopsies